Learning Outcomes
i. Define and differentiate between protostomes and deuterostomes.
ii. Describe the key developmental differences between protostomes and deuterostomes.
iii. Identify examples of protostome and deuterostome animals.
iv. Discuss the evolutionary significance of protostome and deuterostome divergence.
Introduction
Coelomates, the most diverse and complex group of animals, are further classified into two major clades: protostomes and deuterostomes. These two groups exhibit distinct developmental patterns that have shaped their evolutionary trajectories and the diversity of animal life.
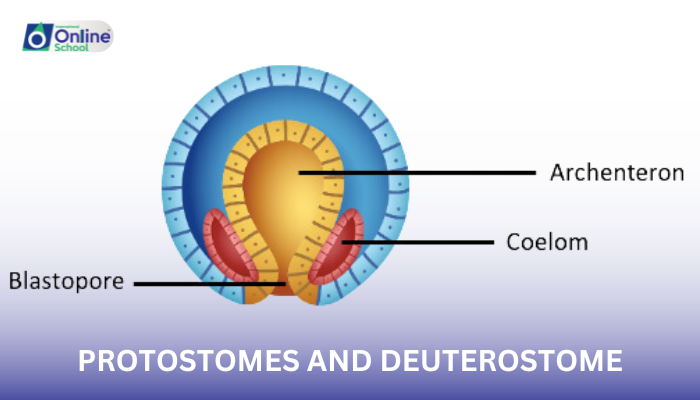
i. Protostomes
Protostomes are characterized by several developmental features:
Spiral Cleavage: During early embryonic development, cell division occurs in a spiral pattern, resulting in faster and more determinate cleavage.
Mouth Formation: The blastopore, the opening at the first stage of embryonic development, forms the mouth, while the anus develops secondarily.
Trochophora Larva: Many protostomes have a specialized larval stage called a trochophore larva, characterized by a ciliated ring and a preoral lobe.
Examples of Protostome Animals:
- Annelids (worms)
- Mollusks (snails, clams)
- Arthropods (insects, spiders, crustaceans)
- Platyhelminthes (flatworms)
- Nematoda (roundworms)
ii. Deuterostomes
Deuterostomes are characterized by distinct developmental features that differ from protostomes:
Radial Cleavage: Early embryonic development involves radial cleavage, where cell division occurs in a vertical pattern, resulting in slower and more indeterminate cleavage.
Mouth Formation: The blastopore forms the anus, while the mouth develops secondarily.
Dipleurula Larva: Many deuterostomes have a specialized larval stage called a dipleurula larva, with a bilateral symmetry and a ciliated band.
Examples of Deuterostome Animals:
- Echinoderms (starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars)
- Chordates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals)
iii. Evolutionary Significance of Protostome and Deuterostome Divergence
The divergence between protostomes and deuterostomes represents a significant evolutionary split that occurred early in animal evolution. The distinct developmental patterns of these two clades have influenced their evolutionary trajectories and contributed to the diversity of animal body plans and developmental processes. Protostomes, with their faster and more determinate cleavage, tend to have highly organized and specialized larval stages, while deuterostomes, with their slower and more indeterminate cleavage, exhibit greater flexibility in development and a wider range of larval forms.
The classification of coelomates into protostomes and deuterostomes based on their developmental differences highlights the evolutionary divergence that has shaped the diversity of animal life. Understanding the unique developmental features of protostomes and deuterostomes provides insights into their evolutionary relationships and the remarkable diversity of animal forms and functions.